Where others see barriers to complex drug delivery to the eye, we see opportunities. We thrive on finding the non-conventional answers that turn your vision into reality.
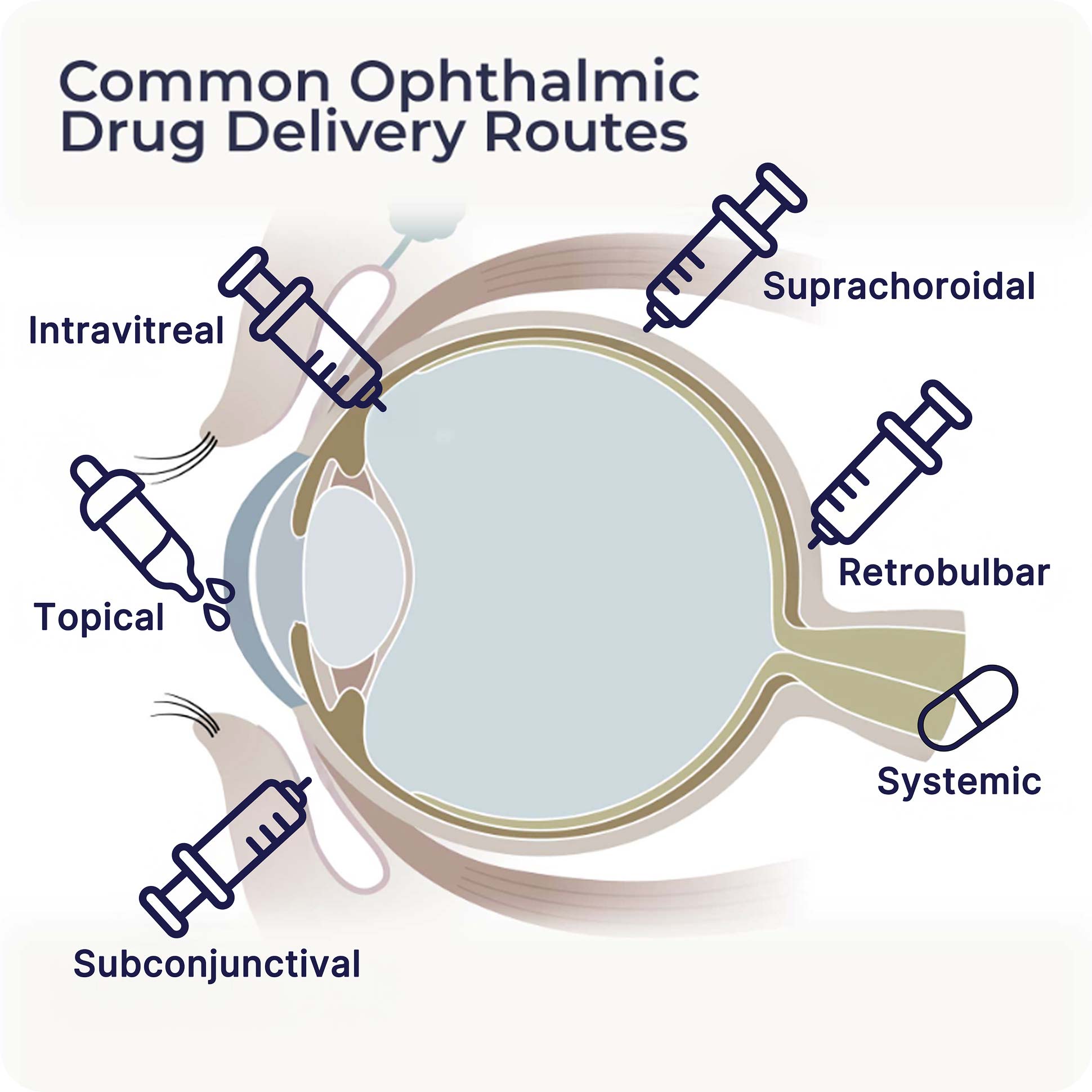
Common Ophthalmic Drug Delivery Routes
- Topical (onto the eye)
- Intravitreal (directly into the vitreous cavity)
- Suprachoroidal (between the choroid and sclera)
- Periocular (into tissues around the eye):
- Retrobulbar (into the retrobulbar space)
- Subconjunctival (under the conjunctiva)
Ophthalmic Drug Development Considerations
Topical Ophthalmic Drug Development Considerations
- Dosage form flexibility: Variety of dosage forms available—including solutions, ointments, and suspension—making it easier to find solutions specific to the drug.
- Penetration enhancers: Careful excipient selection can increase the amount of drug that passes the cornea barrier, including the use of surfactants and fatty acids
- Nanoparticles: Next-gen formulations that can encapsulate a drug and increase bioavailability and its safety profile.
- Viscosity enhancers and bioadhesives: Increase precorneal residence time and ultimately bioavailability of a drug through formulation design.
Intravitreal Injection Drug Development Considerations
- Nanoparticles: ideal route of administration for nanoparticles, which can stabilize a drug extending drug duration and bioavailability in the eye.
- Syringeability & Injectability: drug formulation must be constructed to allow for trouble-free drawing and administration, especially for smaller gauges (e.g., 30G or less)
- Lyophilized Dosage Forms: Drugs with shelf-life stability concerns—especially moisture sensitivity— can be lyophilized.
Suprachoroidal Injection Drug Development Considerations
- High drug concentrations: Formulation design to achieve high drug concentration often necessitated by this route of administration.
- Syringeability & Injectability: Drug formulation needs to be optimized for delivery using micro needles (typically 30-gauiage, 900 µm in length)
- Nanoparticles: as with intravitreal, nanoparticles offer solutions to drug delivery challenges not met by traditional formulations.
Periocular Injection Drug Development Considerations
- Pharmacokinetic Modification: highly influenced by the drug formulation category, with nanoparticle formulations offering significant benefits over traditional formulations
Ophthalmic Formulation Design: Barriers to Ophthalmic Drug Delivery
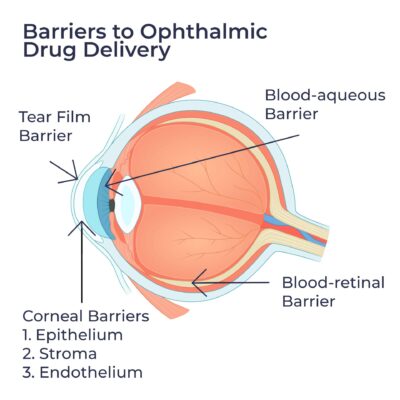 Tear film Barrier – Thin liquid layer that coats the ocular surface serving as the first line of protection. The chemical make up of tears is similar to dilute blood, and contains proteins, enzymes, oils, and electrolytes.
Tear film Barrier – Thin liquid layer that coats the ocular surface serving as the first line of protection. The chemical make up of tears is similar to dilute blood, and contains proteins, enzymes, oils, and electrolytes.
The interaction of a drug with tears is the first barrier to overcome when designing a topical ophthalmic drug formulation.
Corneal Barriers – A multi-layered protective system that works to prevent passage of both hydrophilic (water soluble) and hydrophobic (water insoluble) drugs.
This barrier can be divided into 3 district layers:
1. Epithelium: prevents the passage of hydrophilic drugs and certain large molecules
2. Stroma: prevents the passage of hydrophobic drugs
3. Endothelium: affords selective passage into the aqueous humor for hydrophilic drugs and macromolecules into the aqueous humor
Navigating this complex protective structure requires a delicate balancing act between the water-solubility of the drug and the excipients used in the ophthalmic drug formulation.
Blood-Ocular Barriers – The physical barriers that separates the structures of the eye from the blood stream, which is divided into:
1. Blood-aqueous barrier: epithelium layer located in the anterior portion of the eye which selectively allows for the passage of hydrophobic molecules and smaller molecules.
2. Blood-retinal barrier: posterior portion comprised of retinal endothelial and retinal pigment epithelial cells which controls the passage of molecules in and out of the retina, blocking passage of larger molecules.
Molecular weight of the drug and excipients used in an ophthalmic drug formulation play as important of a role as their physiochemical properties.
Partner with Callan Pharma
Callan Pharma provides its partners rapid, comprehensive and cost-effective solutions for their difficult formulation development projects.


